Abstract
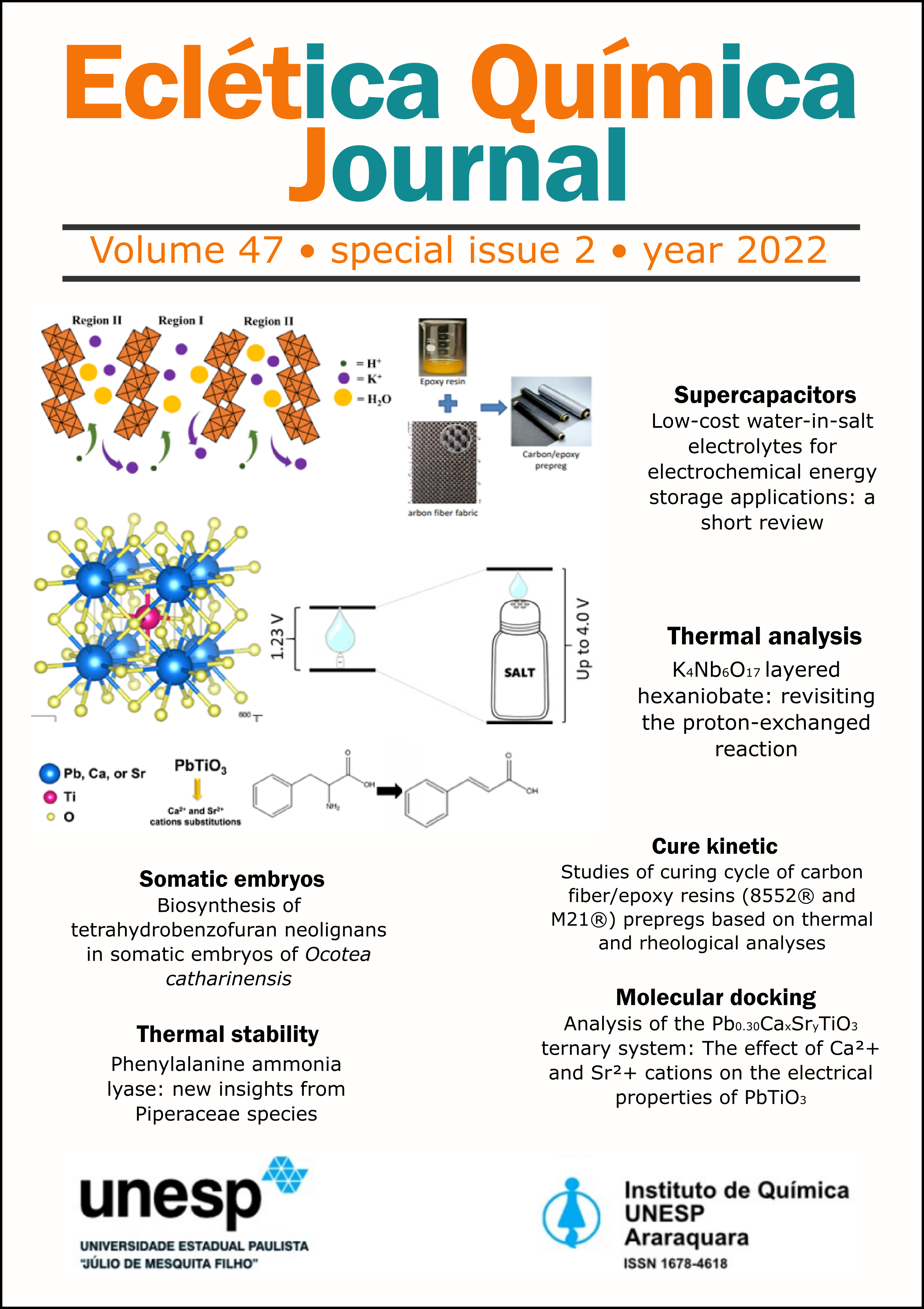
The layered hexaniobate of K4Nb6O17 composition and its derivatives comprise nanostructured materials that exhibit suitable properties for application in catalysis, electrochemistry, and energy, for instance. The exchange of K+ cations to obtain the acidic or protonic niobate form is the main route to originate appropriate precursors to promote the hexaniobate exfoliation, yielding a dispersion of thin layers (2D particles) that can be scrolled under exclusive conditions. Hexaniobate presents two regions (I and II), being the former considered more accessible than region II. In this work, the proton exchange efficiency of the K4Nb6O17 was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis coupled to mass spectrometry (TGA-MS) and metal analysis by inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy (ICP). The products of thermal decomposition profile of the HxK(4-x)Nb6O17 phase were isolated at defined temperature values and characterized by X-ray diffractometry and Raman spectroscopy. The cation exchange percentages obtained by TGA-MS (68.0%) and by quantification of deintercalated K+ by ICP (64.0%) are similar and endorse that region II can also be modified and, consequently, contribute to the exfoliation process.
References
Bizeto, M. A; Constantino, V. R. L.; Structural Aspects and Thermal Behavior of the Proton Exchanged Layered Niobate K4Nb6O17. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39 (11), 1729–1736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2004.05.001
Bizeto, M. A.; Christino, F. P.; Tavares, M. F. M.; Constantino, V. R. L. Aspectos estruturais relacionados ao processo de troca iônica no niobato lamelar K4Nb6O17. Quim. Nova. 2006, 29 (6), 1215-1220. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422006000600013
Bizeto, M. A.; Shiguihara, A. L.; Constantino, V. R. L. Layered niobate nanosheets: building blocks for advanced materials assembly. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19 (17), 2512–2525. https://doi.org/10.1039/b821435b
Bizeto, M. A.; Leroux, F.; Shiguihara, A. L.; Temperini, M. L. A.; Sala, O.; Constantino, V. R. L. Intralamellar structural modifications related to the proton exchanging in K4Nb6O17 layered phase. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2010, 71 (4), 560–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.12.036
Elumalai, S.; Vadivel, S.; Yoshimura, M. Interlayer-modified two-dimensional layered hexaniobate K4Nb6O17 as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2 (6), 1957–1961. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00055A
Gasperin, M.; Le Bihan, M.-T. Un niobate de rubidium d’un type structural nouveau: Rb4Nb6O17·3H2O. J. Solid State Chem. 1980, 33 (1), 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(80)90550-2
Gasperin, M.; Le Bihan, M.T. Mecanisme d’hydratation des niobates alcalins lamellaires de formule A4Nb4O17 (A = K, Rb, Cs). J. Solid State Chem. 1982, 43 (3), 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(82)90251-1
Guo, C.; Zhu, J.; He, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, D. Catalytic oxidation/photocatalytic degradation of ethyl mercaptan on α-MnO2@H4Nb6O17-NS nanocomposite. Vacuum. 2020, 182, 109718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109718
Hu, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Hou, W.; Ding, W. A comparison of H+-restacked nanosheets and nanoscrolls derived from K4Nb6O17 for visible-light degradation of dyes. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23 (2), 136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-4956(14)60128-5
Kimura, N.; Kato, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Shimada, A.; Tahara, S.; Nakato, T.; Matsukawa, K.; Mutin, P.H.; Sugahara, Y. Single- and Double-Layered Organically Modified Nanosheets by Selective Interlayer Grafting and Exfoliation of Layered Potassium Hexaniobate. Langmuir. 2014, 30 (4), 1169–1175. https://doi.org/10.1021/la404223x
Li, D.; Li, Q.; He, J.; Hu, L.; Hu, J. Niobate nanoscroll composite with Fe2O3 particles under moderate conditions: assembly and application research. New J. Chem. 2016, 40 (1), 136–143. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02120K
Liu, X.; Que, W.; Chen, P.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Zhou, H.; Kong, L. B. Facile preparation of protonated hexaniobate nanosheets and its enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanotechnology. 2017, 28 (23), 235702. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa6b4f
Madaro, F.; Sæterli, R.; Tolchard, J.; Einarsrud, M.-A.; Holmestad, R.; Grande, T. Molten salt synthesis of K4Nb6O17, K2Nb4O11 and KNb3O8 crystals with needle- or plate-like morphology. CrystEngComm. 2011, 13 (5), 1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CE00413H
Maeda, K.; Eguchi, M.; Lee, S.-H. A.; Youngblood, W. J.; Hata, H.; Mallouk, T. E. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from Hexaniobate Nanoscrolls and Calcium Niobate Nanosheets Sensitized by Ruthenium(II) Bipyridyl Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009, 113 (18), 7962–7969. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp900842e
Müller-Warmuth, W.; Schöllhorn, R. Progress in Intercalation Research. In Physics and Chemistry of Materials with Low-Dimensional Structures; Springer, 1994.
Nassau, K.; Shiever, J. W.; Bernstein, J. L. Crystal Growth and Properties of Mica‐Like Potassium Niobates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1969, 116 (3), 348–353.
Rao, C. N. R.; Raveau, B. Transition Metal Oxides: Structure, Properties, and Synthesis of Ceramic Oxides. Wiley, 1998.
Shiguihara, A. L.; Bizeto, M. A.; Constantino, V. R. L. Exfoliation of layered hexaniobate in tetra(n-butyl)ammonium hydroxide aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 295 (1–3), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.08.040
Shiguihara, A.; Bizeto, M. A.; Constantino, V. R. L. Chemical modification of niobium layered oxide by tetraalkylammonium intercalation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21 (7), 1366–1376. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532010000700024
Silva, C. H. B.; Iliut, M.; Muryn, C.; Berger, C.; Coldrick, Z.; Constantino, V. R. L., Temperini, M. L. A., Vijayaraghavan, A. Ternary nanocomposites of reduced graphene oxide, polyaniline and hexaniobate: Hierarchical architecture and high polaron formation. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2936–2946. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.272
Wei, Q.; Nakato, T. Preparation of a layered hexaniobate–titania nanocomposite and its photocatalytic activity on removal of phenol in water. J. Porous. Mater. 2009, 16 (2), 151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-007-9179-2

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2022 Eclética Química Journal