Abstract
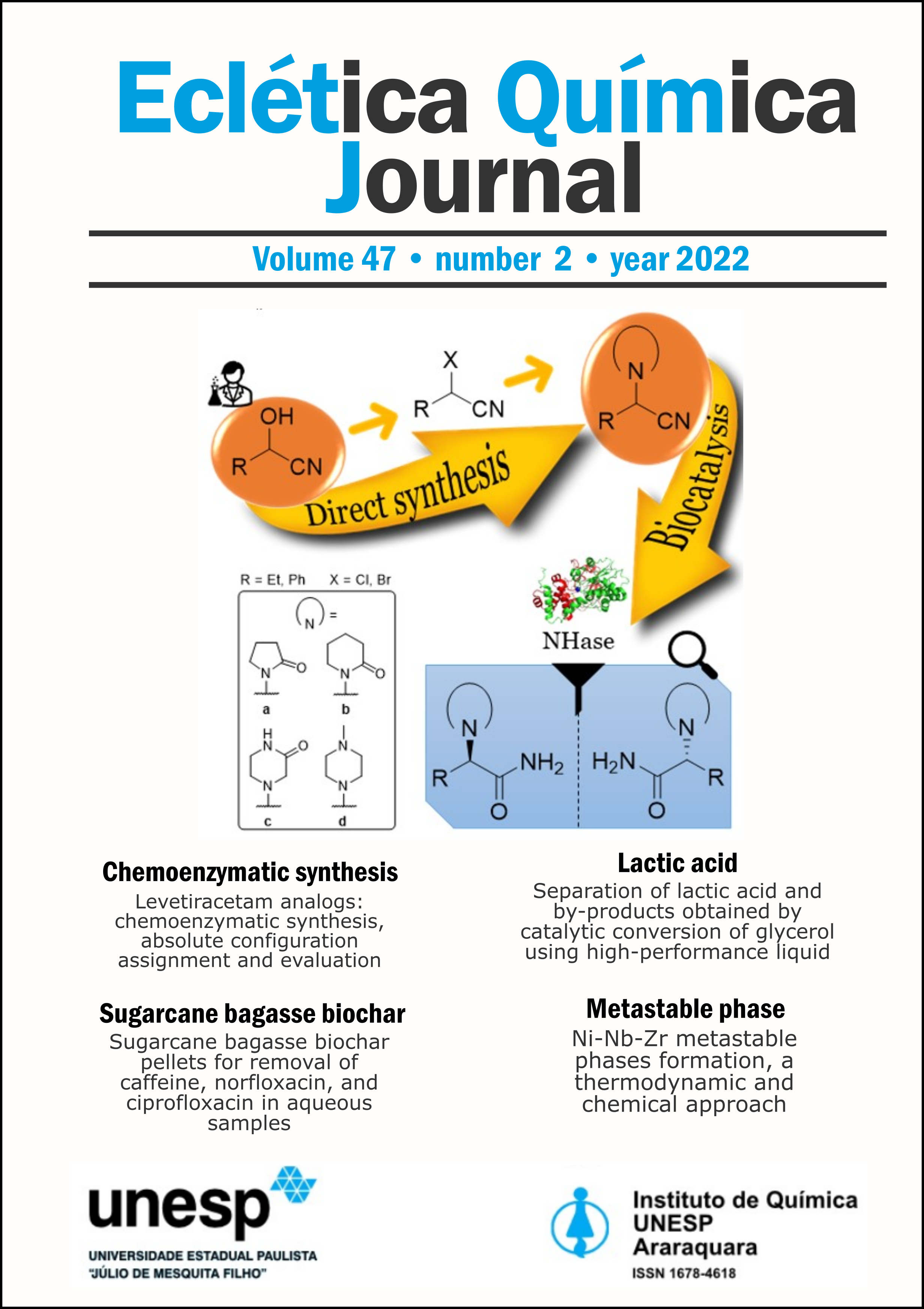
A chemoenzymatic approach for the synthesis of α-N-heterocyclic ethyl- and phenylacetamides, levetiracetam analogs, is described. Eight nitrile substrates were prepared through the N-alkylation of heterocycles (2-pyrrolidinone, 2-piperidinone, 2-oxopiperazine and 1-methylpiperazine) directly from hydroxyl group of ethyl and phenyl α-hydroxynitriles with yield of 35−71% after 12 h. Twenty nitrile hydratases (NHases) were screened and showed that the N-derivatives lactam substrates led to their correspondent amides by Co-type NHase with conversion and enantiomeric excess of up to 47.5 and 52.3% for (S)-enantiomer, while the piperazine substrates underwent spontaneous decomposition by retro-Strecker reaction. In order to avoid a retro-Strecker reaction of α-aminonitriles, ionic liquids and polyethylene glycol (PEG400) were evaluated as alternative green solvents to aqueous buffered solutions in different proportions. Temperature was another parameter investigated during reaction-medium engineering for process optimization. However, unconventional reaction media and low temperature significantly reduced the NHase activity. The absolute configuration of α-N-heterocyclic ethyl- and phenylacetamides, some of which were new compounds, was determined using electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectroscopy. Additionally, their potential as cholinesterase’s inhibitors was evaluated.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.