Abstract
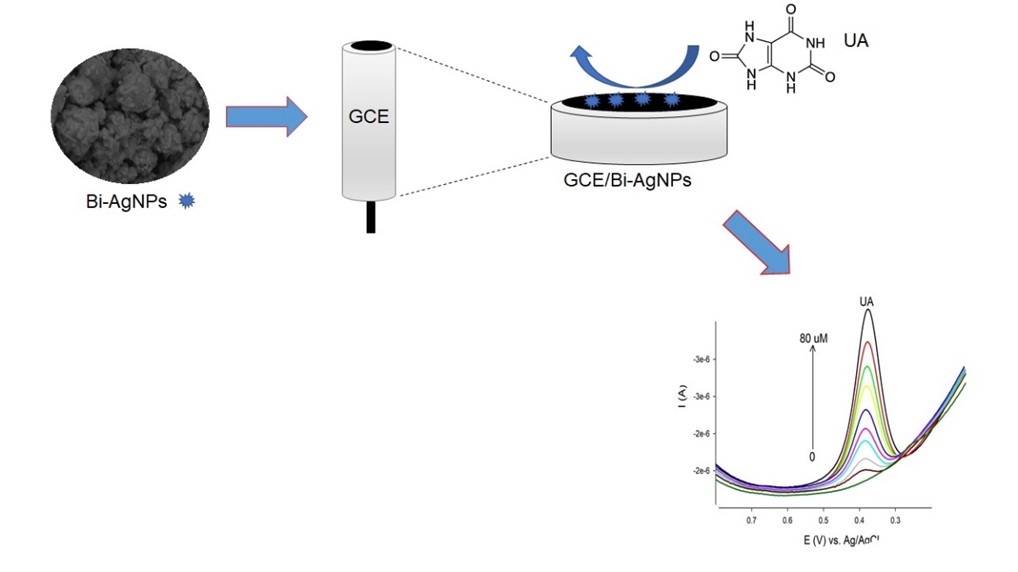
We showcase in this investigation a GCE/Bi–Ag electrochemical nanosensor for uric acid (UA) detection in commercial fruit juice samples. These GCE/Bi–Ag nanosensor electrochemical performances were studied using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) modes showing excellent electrochemical properties toward UA detection in contrast with the clean GCE. Using the fabricated nanosensor, we exploited DPV measurements to detect UA at a meager limit of detection (0.6 μmol/L, S/N = 3) and linearity between 5.0 and 80 μmol/L UA. Furthermore, the GCE/Bi–Ag nanosensor illustrates good repeatability and reproducibility with 3.80% and RSDs of 3.22%, respectively. The GCE/Bi–Ag nanosensor was effectively exploited to determine UA in actual fruit juice samples showing excellent recoveries, indicating that it can be a promising alternative sensor for food analytical applications.
References
Abbas, M. W.; Soomro, R. A.; Kalwar, N. H.; Zahoor, M.; Avci, A.; Pehlivan, E.; Hallam, K. R.; Willander, M. Carbon quantum dot coated Fe3O4 hybrid composites for sensitive electrochemical detection of uric acid. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.034
Ali, A.; Jamal, R.; Abdiryim, T.; Huang, X. Synthesis of monodispersed PEDOT/Au hollow nanospheres and its application for electrochemical determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 787, 110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.01.051
Bai, Z.; Zhou, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Pang, H.; Ma, H. Polyoxometalates-doped Au nanoparticles and reduced grapheneoxide: A new material for the detection of uric acid in urine. Sens. Actuators B. 2017, 243, 361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.159
Beitollahi, H.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Electrocatalytic and simultaneous determination of isoproterenol, uric acid and folic acid at molybdenum (VI) complex-carbon nanotube paste electrode. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 56, 10259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.09.017
Benjamin, S. R.; de Oliveira Neto, J. R.; de Macedo, I. Y. L.; Bara, M. T. F.; da Cunha, L. C.; Carvalho, L. A. F.; Gil, E. S. Electroanalysis for quality control of acerola (Malpighiaemarginata) fruits and their commercial products. Food Anal. Methods. 2015, 8, 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9872-0
Boroumand, S.; Chamjangali, M. A.; Bagherian, G. Double injection/single detection asymmetric flow injection manifold for spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid and uric acid: Selection the optimal conditions by MCDM approach based on different criteria weighting methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A. 2017, 174, 203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.11.031
Brainina, K. Z.; Bukharinova, M. A.; Stozhko, N. Y.; Sokolkov, S. V.; Tarasov, A. V. M.; Vidrevich, M. B. Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Carbon Veil Modified by Phytosynthesized Gold Nanoparticles for Determination of Ascorbic Acid. Sensors. 2020, 20, 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061800
Choi, H. K.; Mount, D. B.; Reginato, A. M. Pathogenesis of gout. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143 (7), 499–516. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-143-7-200510040-00009
Das, T. R.; Sharma, P. K. Hydrothermal-assisted green synthesis of Ni/Ag@rGO nanocomposite using Punica granatum juice and electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104850
Erden, P. E.; Kilic, E. A review of enzymatic uric acid biosensors based on amperometric detection. Talanta. 2013, 107, 312–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.01.043
Fukuda, T.; Muguruma, H.; Iwasa, H.; Tanaka, T.; Hiratsuka, A.; Shimizu, T.; Tsuji, K.; Kishimoto, T. Electrochemical determination of uric acid in urine and serum with uricase/carbon nanotube /carboxymethylcellulose electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 590, 113533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113533
Ganesh, P. S.; Kumara Swamy, B. E. Simultaneous electroanalysis of norepinephrine, ascorbic acid and uric acid using poly(glutamic acid) modified carbon paste electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 752, 17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.06.002
Hou, J.; Xu, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J. Facile fabrication of hierarchical nanoporous AuAg alloy and its highly sensitive detection towards dopamine and uric acid. Sens Actuators B. 2016, 225, 241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.11.035
Huang, S. H.; Shih, Y. C.; Wu, C. Y.; Yuan, C. J.; Yang, Y. S.; Li, Y. K.; Wu, T. K. Detection of serum uric acid using the optical polymeric enzyme biochip system. Biosens Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2003.12.026
Kanbay, M.; Jensen, T.; Solak, Y.; Le, M.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.; Rivard, C.; Lanaspa, M. A.; Nakagawa, T.; Johnson, R. J. Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: from an innocent bystander to a central player. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016. 29, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2015.11.026
Lakshmi, D.; Whitcombe, M. J.; Davis, F.; Sharma, P. S.; Prasad, B. B. Electrochemical detection of uric acid in mixed and clinical samples: a review. Electroanalysis. 2011, 23, 305–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201000525
Laviron, E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1979, 101, 19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(79)80075-3
Li, X. L.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y. Z.; Kang, D.; Jin, H.; Shi, Q.; Jin, T.; Inoue, K.; Todoroki, K.; Toyo'Oka, T. Human nails metabolite analysis: A rapid and simple method for quantification of uric acid in human fingernail by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV-detection. J. Chromatogr. B. 2015, 1002, 394–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.08.044
Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, B-C. A novel electrochemical sensor based on bimetallic metal–organic framework-derived porous carbon for detection of uric acid. Talanta. 2019, 199, 478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.008
Luo, X.; Cai, N.; Cheng, Z. Determination of Uric Acid in Plasma by LC–MS/MS and Its Application to an Efficacy Evaluation of Recombinant Urate Oxidase. Anal. Sci. 2013, 29, 709–713. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.29.709
Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L. PtNi bimetallic nanoparticles loaded MoS2 nanosheets: Preparation and electrochemical sensing application for the detection of dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2019, 1055, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.025
Mahmoudian, M. R.; Basirun, W. J.; Sookhakian, M.; Woi, P. M.; Zalnezhad, E.; Hazarkhani, H.; Alias, Y. Synthesis and characterization of a-Fe2O3/polyaniline nanotube composite as electrochemical sensor for uric acid detection. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.11.015
Makombe, M.; Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Antimony film sensor for sensitive rare earth metal analysis in environmental samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A. 2016, 8, 597–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2016.1159857
Misra, N.; Kumar, V.; Borde, L.; Varshney, L. Localized surface plasmon resonance-optical sensors based on radiolytically synthesized silver nanoparticles for estimation of uric acid. Sens. Actuators B. 2013, 178, 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.110
Papavasileiou, M. V.; Karamanou, A. G.; Kalogeropoulos, P.; Moustakas, G.; Patsianis, S.; Pittaras, A. Uric acid blood levels and relationship with the components of metabolic syndrome in hypertensive patients. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 414–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.53
Raj, C. R.; Ohsaka, T. Electroanalysis of ascorbate and dopamine at a gold electrode modified with a positively charged self-assembled monolayer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 496 (1–2), 44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(00)00335-1
Rajesh, M.; Yan, W-M.; Yen, Y-K. Solvothermal synthesis of two‑dimensional graphitic carbon nitride/tungsten oxide nanocomposite: a robust electrochemical scaffold for selective determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2022, 52, 1231–1248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01699-6
Riches, P. L.; Wright, A. F.; Ralston, S. H. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of hyperuricaemia and gout. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, R177–R184. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp369
Sadikoglu, M.; Taskin, G.; Demirtas, F. G.; Selvi, B.; Barut, M. Voltammetric Determination of Uric Acid on Poly(p-Aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid)-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7 (11), 11550–11557.
Sangamithirai, D.; Munusamy, S.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A. A voltammetric biosensor based on poly(o-methoxyaniline)-gold nanocomposite modified electrode for the simultaneous determination of dopamine and folic acid. Mater Sci. Eng. C. 2018, 91, 512–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.05.070
Silwana, B.; Van der Horst, C.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Reduced Graphene Oxide Impregnated Antimony Nanoparticle Sensor for Electroanalysis of Platinum Group Metals. Electroanalysis. 2016, 28 (7), 1597–1607. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201501071
Tadesse, Y.; Tadese, A.; Saini, R. C.; Pal, R. Cyclic Voltammetric Investigation of Caffeine at Anthraquinone Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Int J. Electrochem. 2013, 2013, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/849327
Van der Horst, C. Development of a Bismuth-Silver Nanofilm Sensor for the Determination of Platinum Group Metals in Environmental Samples. PhD’s Thesis, University of the Western Cape: Bellville, South Africa, 2015.
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Synthesis and characterisation of bismuth-silver bimetallic nanoparticles for electrochemical sensor applications. Anal. Lett. 2015a, 48, 1311–1332. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2014.979357
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Bismuth-silver bimetallic nanosensor application for the voltammetric analysis of dust and soil samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015b, 752, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.06.001
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Application of a bismuth-silver nanosensor for the simultaneous determination of Pt-Rh and Pd-Rh complexes. J. Nano Res. 2016a, 44, 126–133. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.44.126
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Gil, E.; Somerset, V. Improved detection of ascorbic acid with a bismuth-silver nanosensor. Food Anal. Method. 2016b, 9, 2560–2566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0444-3
Van der Horst, C. Silwana, B. Iwuoha, E. Somerset, V. Voltammetric analysis of platinum group metals using a bismuth-silver bimetallic nanoparticles sensor. In. Recent Progress in Organometallic Chemistry, Chapter 6; Rahman, M. M., Asiri, A. M.; Eds.; INTECH, Croatia, 2017a; pp 123. https://doi.org/10.5772/68132
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Electrocatalytic evaluation of a horseradish peroxidase biosensor based on a novel Bi-Ag bimetallic nanocomposite. Proc. Technol. 2017b, 27, 179–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2017.04.077
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Spectroscopic and voltammetric analysis of platinum group metals in road dust and roadside soil. Environments. 2018, 5 (11), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5110120
Van der Horst, C.; Silwana, B.; Gil, E.; Iwuoha, E.; Somerset, V. Simultaneous Detection of Paracetamol, Ascorbic Acid, and Caffeine Using a Bismuth-Silver Nanosensor. Electroanalysis. 2020, 32, 3098–3107. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060389
Van der Horst, C.; Somerset, V. Nanoparticles Application in the Determination of Uric Acid, Ascorbic Acid, and Dopamine. Russian J. Electrochem. 2022, 58, 341–359. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319352205010X
Wan, W.; Xu, X.; Zhao, D. B.; Pang, Y. F.; Wang, Y. X. Polymorphisms of uric transporter proteins in the pathogenesis of gout in a Chinese Han population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14 (1), 2546–2550. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.March.30.13
Wang, H.; Cao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Tong, Z. A facile approach to synthesis methylene blue/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2022, 52, 1067–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01695-w
Wayu, M. B.; Di Pasquale, L. T.; Schwarzmann, M. A.; Gillespie, S. D.; Leopold, M. C. Electropolymerization of β-cyclodextrin onto multi-walled carbon nanotube composite films for enhanced selective detection of uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 783, 192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.11.021
Yue, H. Y.; Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, S.; Yao, L. H.; Lin, X. Y.; Guo, E. J. Highly sensitive and selective uric acid biosensor based on a three-dimensional graphene foam/indium tin oxide glass electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 488, 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2015.07.007
Zhang, K.; Chena, X.; Lia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Guo, T.; Zhang, D.; Xue, Z.; Zhou, Lu, X. Au-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles decorated on sulfonated nitrogen sulfur co-doped graphene for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Talanta. 2018, 178, 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.047
Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y-C.; Ma, L-X. One-pot facile fabrication of graphene-zinc oxide composite and its enhanced sensitivity for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B. 2016, 227, 488–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.073
Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.; Qin, L.; Jia, H.; Liu, S. Synthesis of Ta/Ni microcavity array film for highly sensitive uric acid detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 834, 86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.12.053

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Eclética Química